NUTRACENTER BLOG
Inflammatory Foods Your Should Avoid
Boosting your metabolism is like hitting the jackpot for weight loss and better health. A faster metabolism helps your body burn calories more efficiently, aiding in weight management and energy levels. Fortunately, certain foods can rev up your metabolic engine. Here are the top 10 foods known for their metabolism-boosting properties.
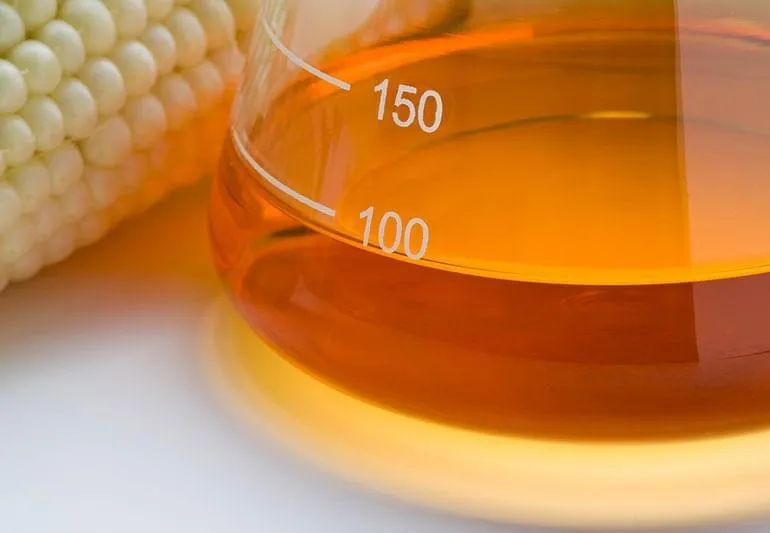

1. Sugar and High-Fructose Corn Syrup
Sugar (sucrose) and high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) are found in many processed foods and beverages. Excessive consumption of these sweeteners can lead to inflammation, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of several diseases.

2. Artificial Trans Fats
Unlike natural trans fats found in dairy and meat, artificial trans fats, or partially hydrogenated oils, are notorious for their inflammatory effects. They can increase bad cholesterol levels, lower good cholesterol levels, and are linked to a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
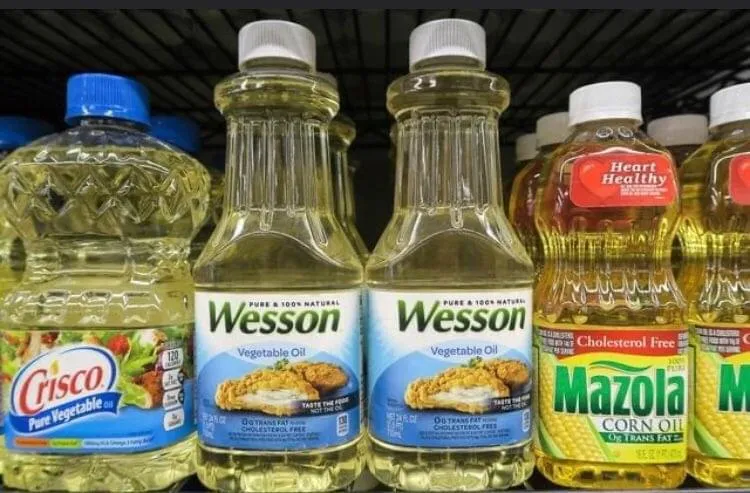

3. Vegetable and Seed Oils
Some vegetable oils, such as soybean, corn, sunflower, and cottonseed oils, are high in omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-6s are essential in moderation, excessive amounts can lead to inflammation, especially when the balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids is skewed.
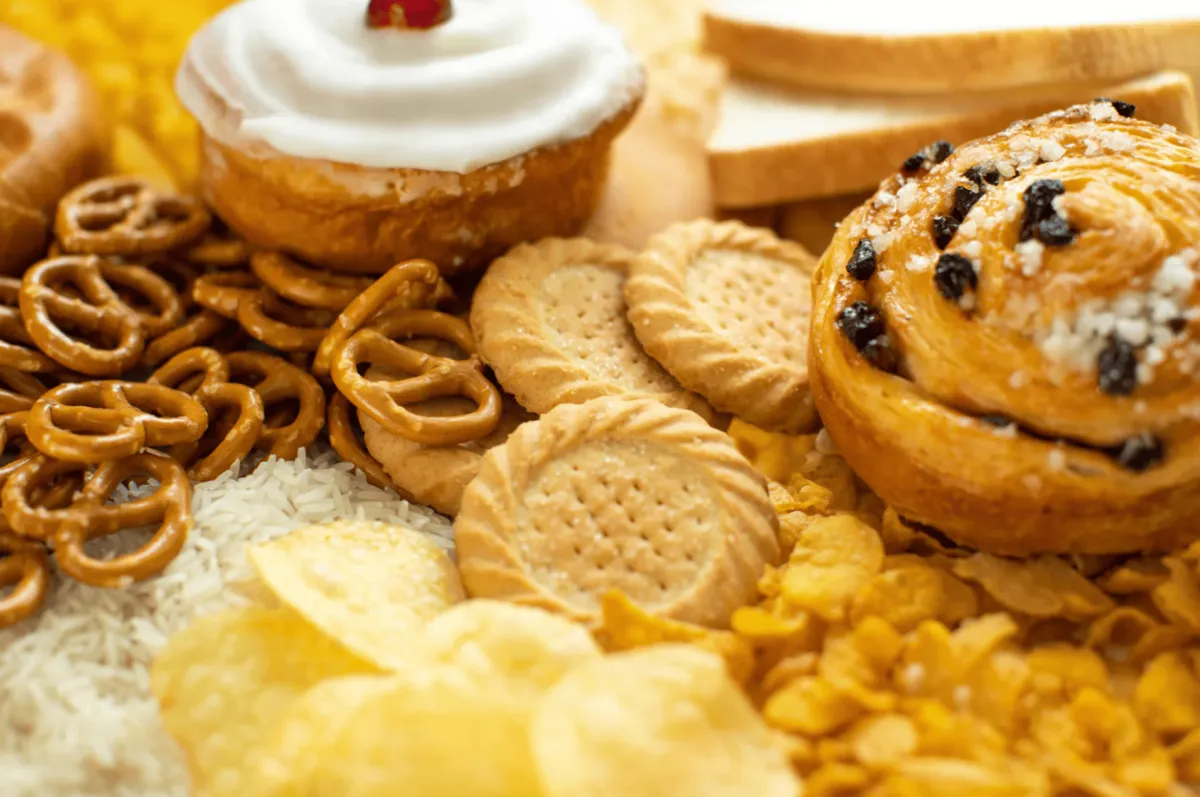

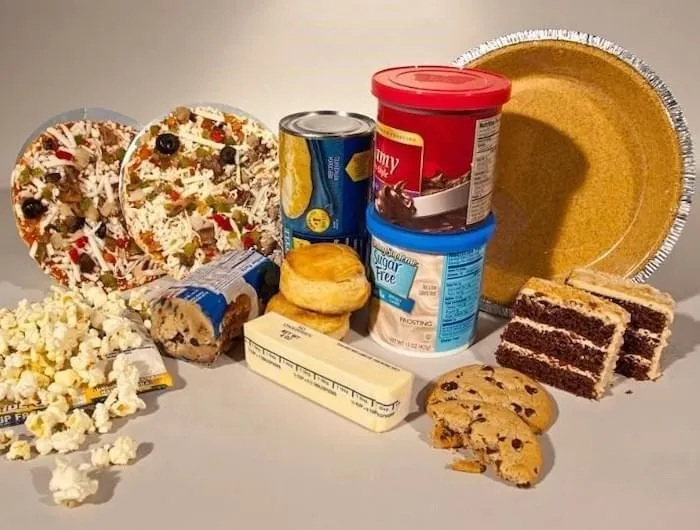
4. Refined Carbohydrates
White bread, white rice, pastries, snacks, and other refined carbohydrates have a high glycemic index. They can spike blood sugar levels and lead to an increase in inflammation. These foods lack fiber, which helps reduce inflammation and stabilize blood sugar levels.
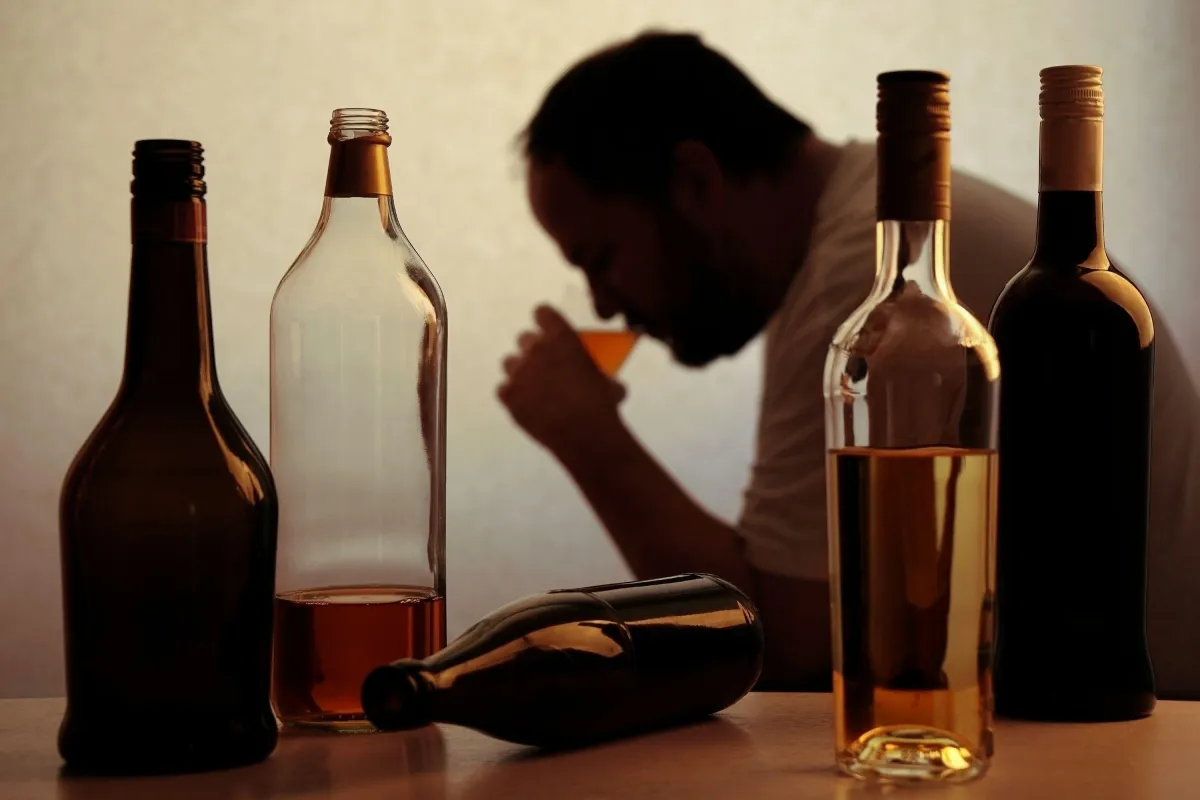

5. Excessive Alcohol
Moderate alcohol consumption may have some health benefits. However, high amounts can lead to a significant inflammatory response and potentially damage your liver, brain, and other organs.
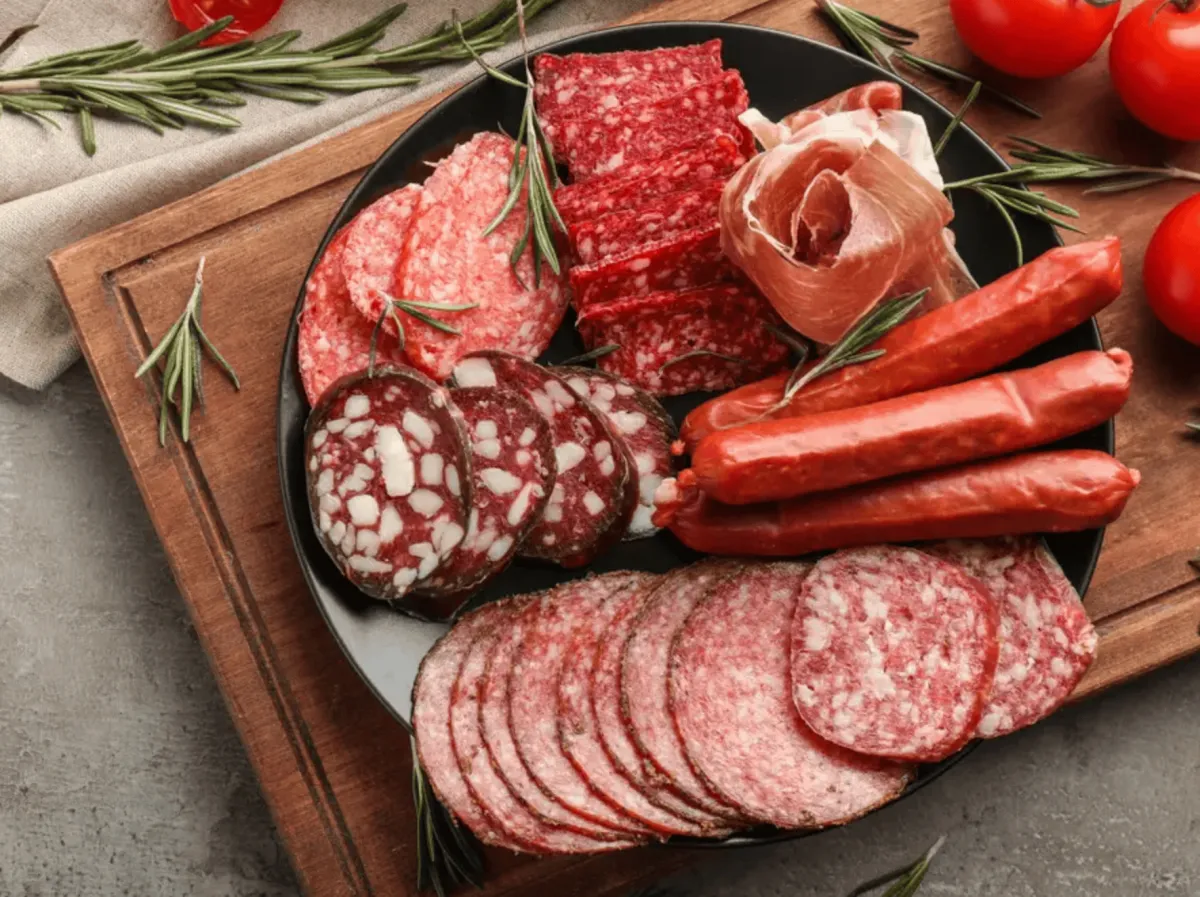

6. Processed Meat
Processed meats, such as sausages, bacon, ham, and smoked meat, contain more advanced glycation end products (AGEs) than most other meats. AGEs are formed when meat is cooked at high temperatures and can trigger inflammation.
7. Gluten for Sensitive Individuals
For people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, gluten — found in wheat, barley, and rye — can trigger a harmful inflammatory response. Even without diagnosed sensitivity, some individuals may feel better reducing gluten in their diet.
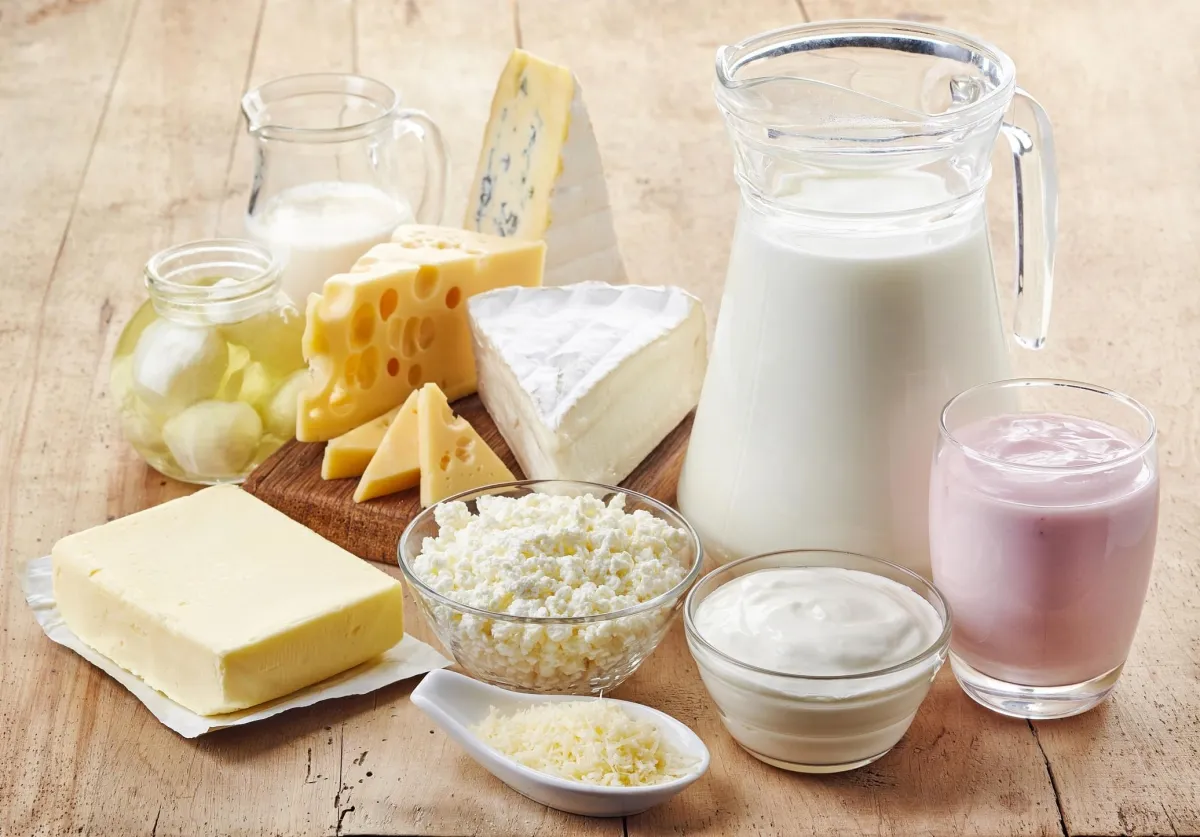

8. Dairy Products for Sensitive Individuals
Similarly, some people are sensitive to the proteins found in dairy, such as casein and whey. This sensitivity can cause inflammatory responses, including bloating, stomach pain, and diarrhea.

9. Artificial Sweeteners
Though often marketed as a healthier alternative to sugar, some artificial sweeteners may trigger inflammation and adverse effects in some people, including disrupting gut health and glucose tolerance.

10. Junk Food and Fast Food
High in trans fats, refined carbohydrates, and added sugars, these foods are not only inflammatory but also contribute to obesity, a known risk factor for inflammation.
Inflammation can be both a friend and a foe. While acute inflammation is a necessary part of the healing process, chronic inflammation can lead to numerous health issues. Paying attention to your diet is a key strategy in managing inflammation. By avoiding or reducing the intake of the foods listed above, you can help minimize your risk of inflammation-related diseases and improve your overall health. Always consider a balanced diet rich in whole foods, vegetables, fruits, lean protein, and healthy fats to support your body's well-being.

For Product & Order Support, please contact us here.
a NUTRACENTER brand
